Variants: Production Models


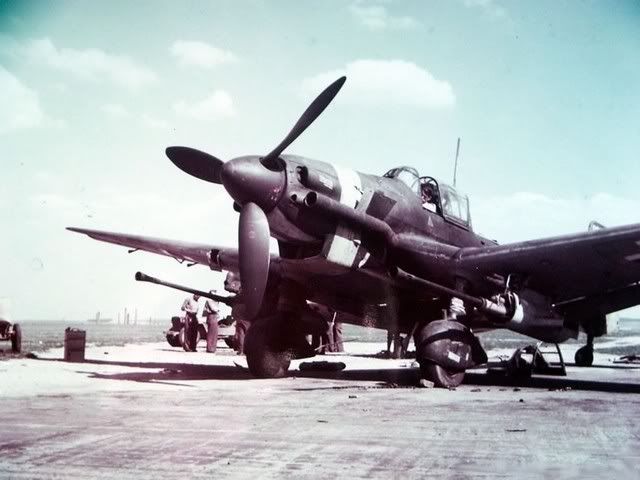
Ju 87B "Bertha"
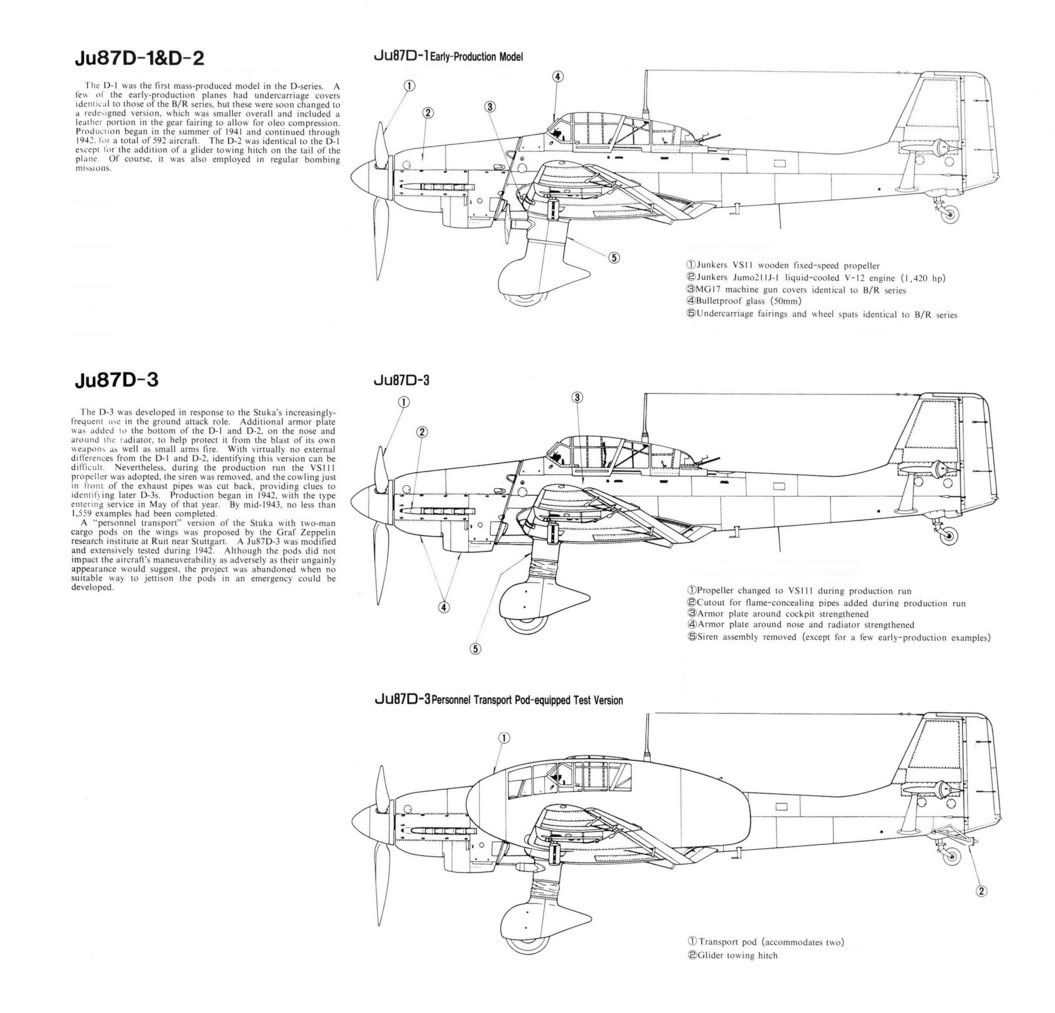
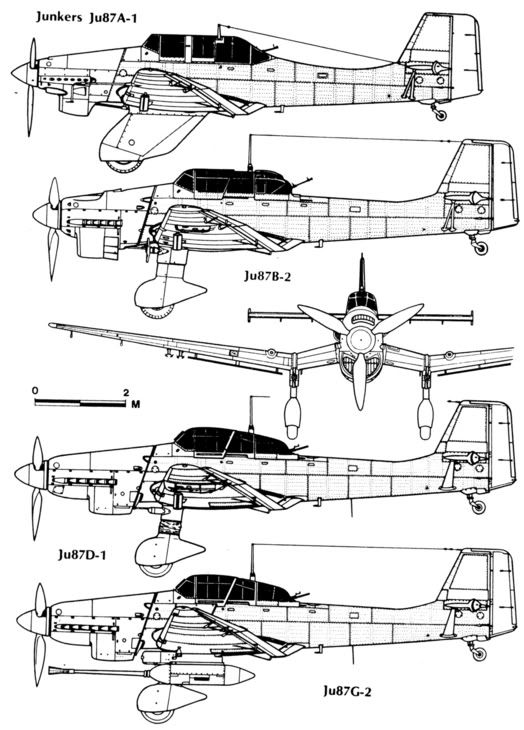
The Ju 87 B series was to be the first mass-produced variant. A total of six pre-production Ju 87 B-0 were produced, built from Ju 87 A airframes. Test flights began from the summer of 1937. A small number, at least three, served as conversion Cs or Es for potential naval variants.

Junker Ju 87B.
[Source: Unknown]
The first production version was the Ju 87 B-1, with a considerably larger engine, its Junkers Jumo 211D generating 1,200 PS (883 kW, 1,184 hp), and completely redesigned fuselage and landing gear. This new design was again tested in Spain, and after proving its abilities there, production was ramped up to 60 per month. As a result, by the outbreak of World War II, the Luftwaffe had 336 Ju 87 B-1s on hand.

The B-1 was also fitted with "Jericho trumpets", essentially propeller-driven sirens with a diameter of 0.7 m (2.3 ft) mounted on the wing's leading edge directly forward of the landing gear, or on the front edge of the fixed main gear fairing. This was used to weaken enemy morale and enhance the intimidation of dive-bombing. After the enemy became used to it, however, they were withdrawn. The devices caused a loss of some 20–25 kph (10-20 mph) through drag. Instead, some bombs were fitted with whistles on the fin to produce the noise after release.

The trumpets were a suggestion from Generaloberst Ernst Udet (but some authors say the idea originated from Adolf Hitler). The Ju 87 B-2s that followed had some improvements and were built in a number of variants that included ski-equipped versions (the B-1 also had this modification), and at the other end, with a tropical operation kit called the Ju 87 B-2 trop.
Italy's Regia Aeronautica received a number of the B-2s and named them the "Picchiatello", while others went to the other members of the Axis, including Hungary, Bulgaria and Romania. The B-2 also had an oil hydraulic system for closing the cowling flaps. This continued in all the later designs.
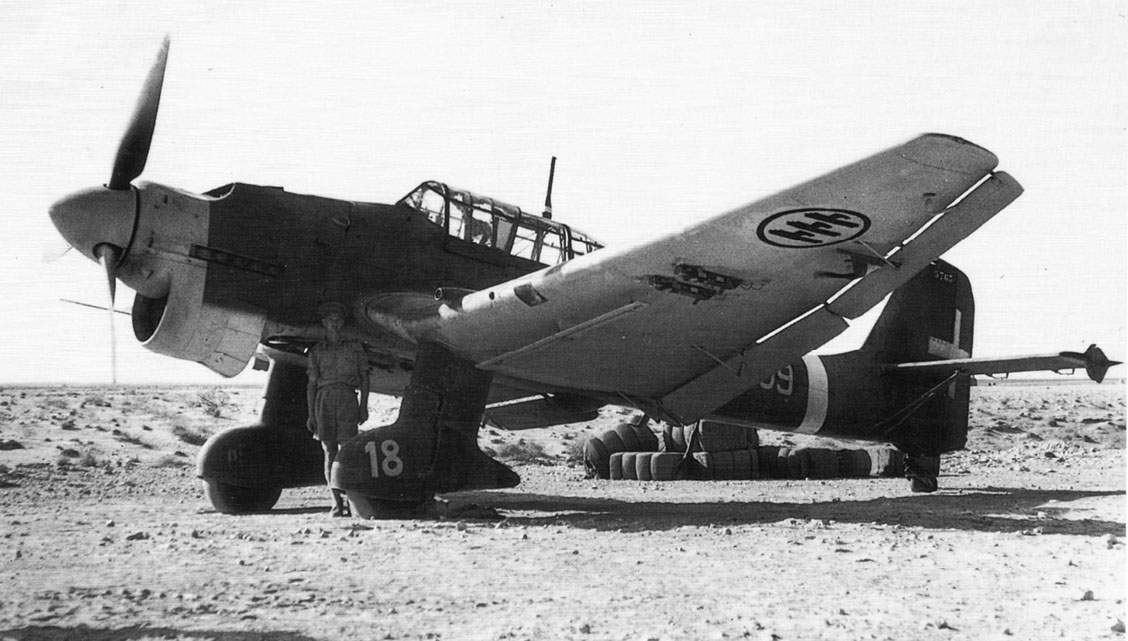

Italian Air force Ju87B2-trop, forced down behind British Lines
The tropicalised versions were initially named the Ju 87 B-2/U1. This was eventually designated the Ju 87 B-2 trop, equipped with tropical emergency equipment and sand filters for the powerplant.
Production of the Ju 87 B started in 1937. 89 B-1s were to be built at Junkers' factory in Dessau and another 40 at the Weserflug plant in Lemwerder by July 1937. Production would be carried out by the Weserflug company after April 1938, but Junkers continued producing Ju 87 up until March 1940. Total production amounted to 697 B-1s (311 by Junkers, 386 by Weserflug) and 225 B-2s (56 by Junkers, 169 by Weserflug). The last Ju 87B rolled off the production lines in October 1940.
Ju 87R
A long range version of the Ju 87 B was also built, known as the Ju 87 R. They were primarily intended for anti-shipping missions. The Ju 87R had a B-series airframe with an additional oil tank and fuel lines to the outer wing stations to permit the use of two 300 L (79,25 US gal) under-wing drop tanks.
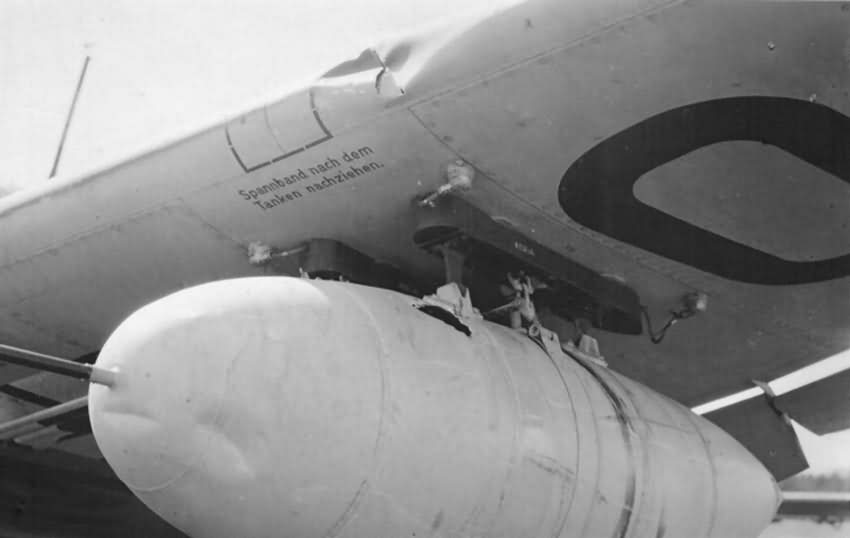

This increased fuel capacity to 1,080 litres (500 L in main fuel tank of which 480 L where usable + 600 L from drop tanks). To prevent overload conditions, bomb carrying ability was often restricted to a single 250 kg (550 lb) bomb if the aircraft was fully loaded with fuel.
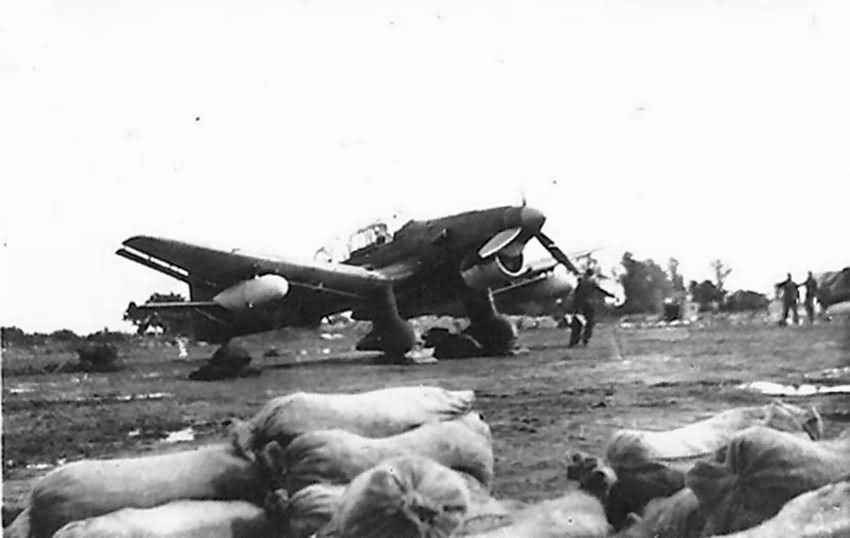

Ju 87 R-3
The Ju 87 R-1 had a B-1 airframe with the exception of a modification in the fuselage which enabled an additional oil tank. This was installed to feed the engine due to the increase in range after the addition of the extra fuel tanks.
The Ju 87 R-2 had the same airframe as the B-2, and strengthened to ensure it could withstand dives of 600 kph (370 mph). The Jumo 211D in-line engine was installed, replacing the R-1s Jumo 211A. Due to an increase in overall weight by some 700 kg (1,540 lb), the Ju 87 R-2 was 30 kph (20 mph) slower than the Ju 87 B-1 and had a lower service ceiling. The Ju 87 R-2 had an increased range advantage of 360 km (220 mi). The R-3 and R-4 were the last R variants developed. Only a few were built.
The R-3 was an experimental tug for gliders and had an expanded radio system so the crew could communicate with the glider crew by way of the tow rope. The R-4 differed from the R-2 in the Jumo 211J powerplant.
Total production amounted to 972 Ju 87R (105 R-1, 472 R-2, 144 R-4), all built by Weserflug. The last Ju 87R rolled off the production lines in October 1941.
Ju 87 C

Ju 87 R2
On 18 August 1937, the RLM decided to introduce the Ju 87 Tr(C). The Ju 87 C was intended to be a dive and torpedo bomber for the Kriegsmarine. The type was ordered into prototype production and available for testing in January 1938. Testing was given just two months and was to begin in February and end in April 1938. The prototype V10 was to be a fixed wing test aircraft, while the following V11 would be modified with folding wings. The prototypes were Ju 87 B-0 airframes powered by Jumo 211 A engines. Owing to delays, the V10 was not completed until March 1938. It first flew on 17 March and was designated Ju 87 C-1. On 12 May, the V11 also flew for the first time. By 15 December 1939, 915 arrested landings on dry land had been made. It was found the arresting gear winch was too weak and had to be replaced. Tests showed the average braking distance was 20–35 metres (65–115 feet). The Ju 87 V11 was designated C-0 on 8 October 1938. It was fitted out with standard Ju 87C-0 equipment and better wing-folding mechanisms. The "carrier Stuka" was to be built at the Weserflug Company's Lemwerder plant between April and July 1940.

Among the "special" equipment of the Ju 87 C was a two-seat rubber dinghy with signal ammunition and emergency ammunition. A quick fuel dump mechanism and two inflatable 750 L (200 US gal) bags in each wing and a further two 500 L (130 US gal) bags in the fuselage enabled the Ju 87 C to remain afloat for up to three days in calm seas. On 6 October 1939, with the war already underway, 120 of the planned Ju 87 Tr(C)s on order at that point were cancelled. The intention was to launch them off the Graf Zeppelin CV1 class aircraft carriers:
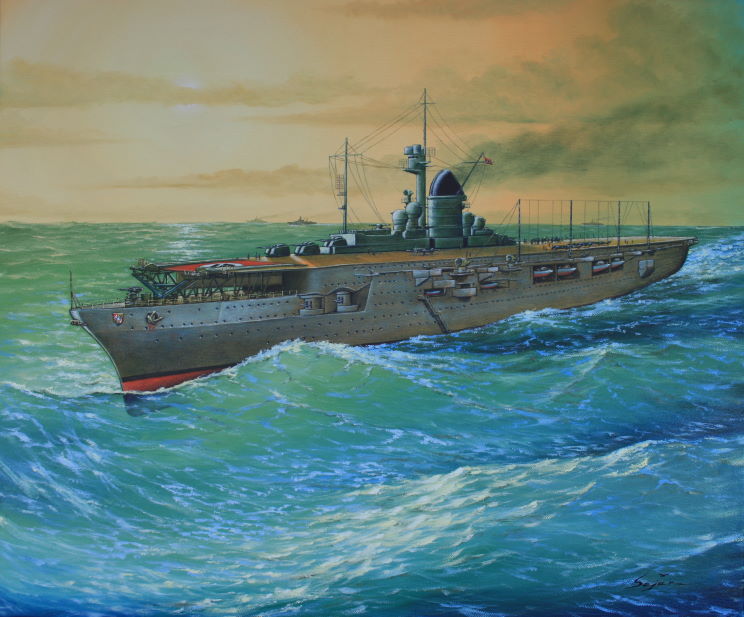
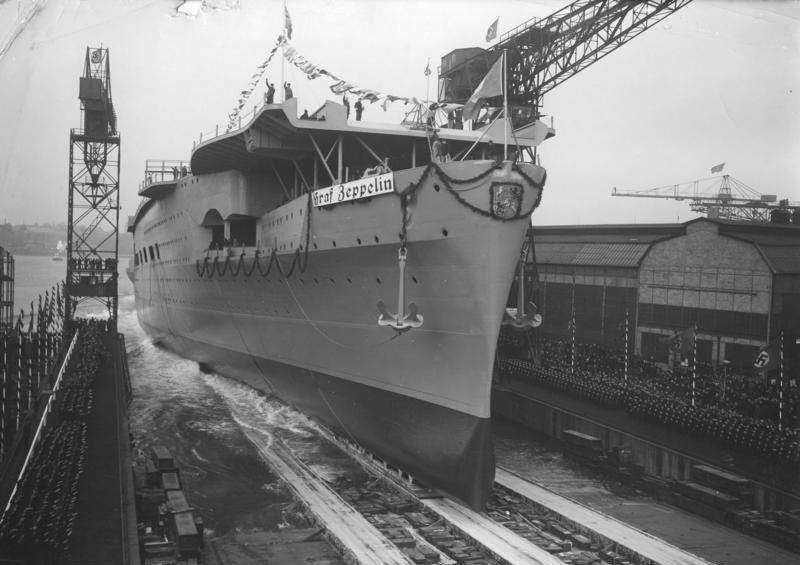



Despite the cancellation, the tests continued using catapults:

The Ju 87 C had a takeoff weight of 5,300 kg (11,700 lb) and a speed of 133 kph (82 mph) on departure. The Ju 87 could be launched with a SC 500 kg (1,100 lb) bomb and four SC 50 kg (110 lb) bombs under the fuselage. The C-1 was to have two MG 17s mounted in the wing with a MG 15 operated by the rear gunner. On 18 May 1940, production of the C-1 was switched to the R-1.

Junkers Ju 87 C.
Ju 87D "Dora"

Ju 87 D-5
Despite the Stuka's vulnerability to enemy fighters having been exposed during the Battle of Britain, the Luftwaffe had no choice but to continue its development, as there was no replacement aircraft in sight. The result was the D-series. In June 1941, the RLM ordered five prototypes, the Ju 87 V21–25. A Daimler-Benz DB 603 powerplant was to be installed in the Ju 87 D-1, but it did not have the power of the Jumo 211 and performed "poorly" during tests and was dropped. The Ju 87 D-series featured two coolant radiators underneath the inboard sections of the wings, while the oil cooler was relocated to the position formerly occupied by the coolant radiator.
The D-series also introduced an aerodynamically refined cockpit with better visibility and space. In addition, armor protection was increased and a new dual-barrel 7.92 mm MG 81Z machine gun with an extremely high rate of fire was installed in the rear defensive position. Engine power was increased again, the Ju mo 211J now delivering 1,420 PS (1,044 kW, 1,401 hp). Bomb carrying ability was nearly quadrupled from 500 kg (1,100 lb) in the B-version to 1,800 kg (3,970 lb) in the D-version (max. load for short ranges, overload condition), a typical bomb load ranged from 500-1,200 kg (1,100-2,650 lb).
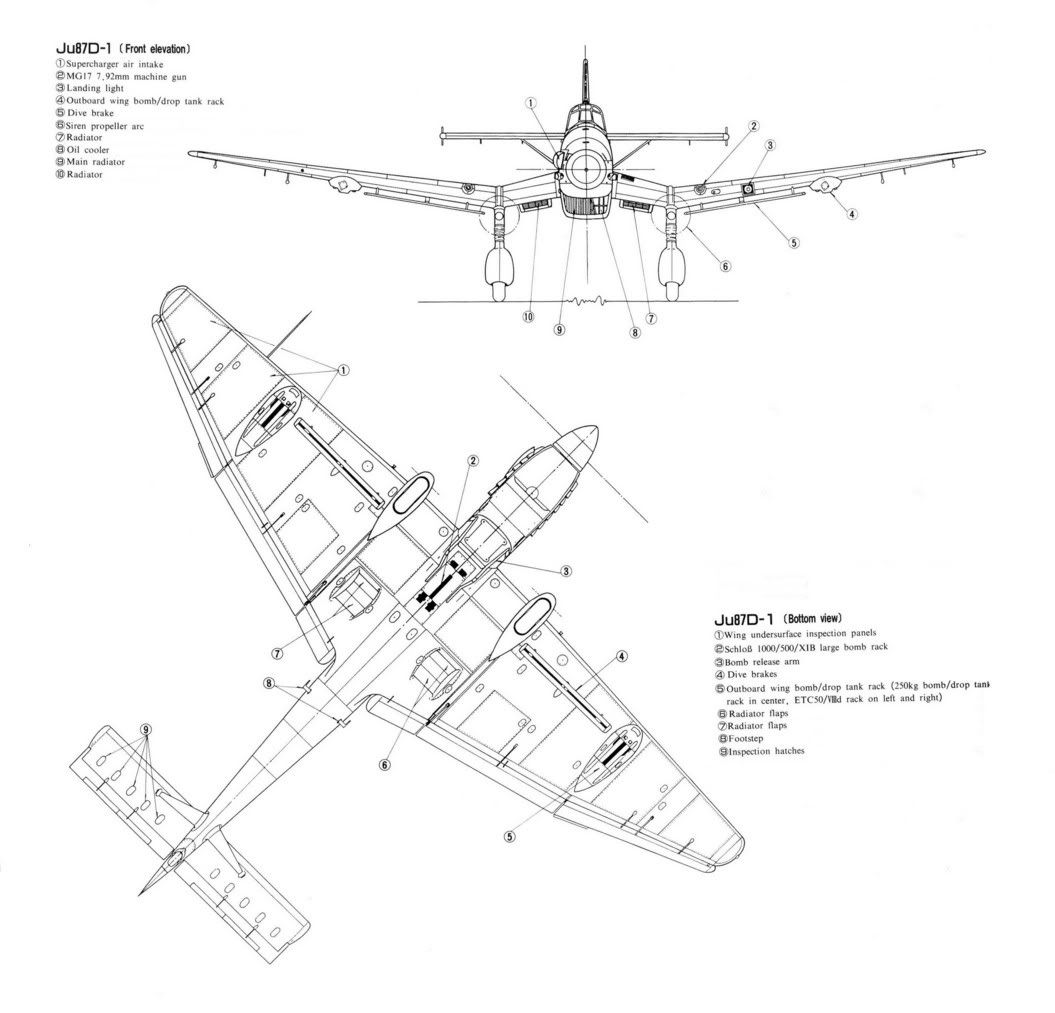

The D-2 was a variant used as a glider tug by converting older D-series airframes. It was intended as the tropical version of the D-1 and had heavier armour to protect the crew from ground fire. The armour reduced its performance and caused the Oberkommando der Luftwaffe to "place no particular value on the production of the D-2".
The D-3 was an improved D-1 with more armour for its ground-attack role. A number of Ju 87 D-3s were designated D-3N or D-3 trop and fitted with night or tropical equipment. The D-4 designation applied to a prototype torpedo-bomber version, which could carry a 750–905 kg (1,650-2,000 lb) aerial torpedo on a PVC 1006 B rack.
The D-4 was to be converted from D-3 airframes and operated from the aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin. Other modifications included a flame eliminator and, unlike earlier D variants, two 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon, while the radio operator/rear gunner's ammunition supply was increased by 1,000 to 2,000 rounds.

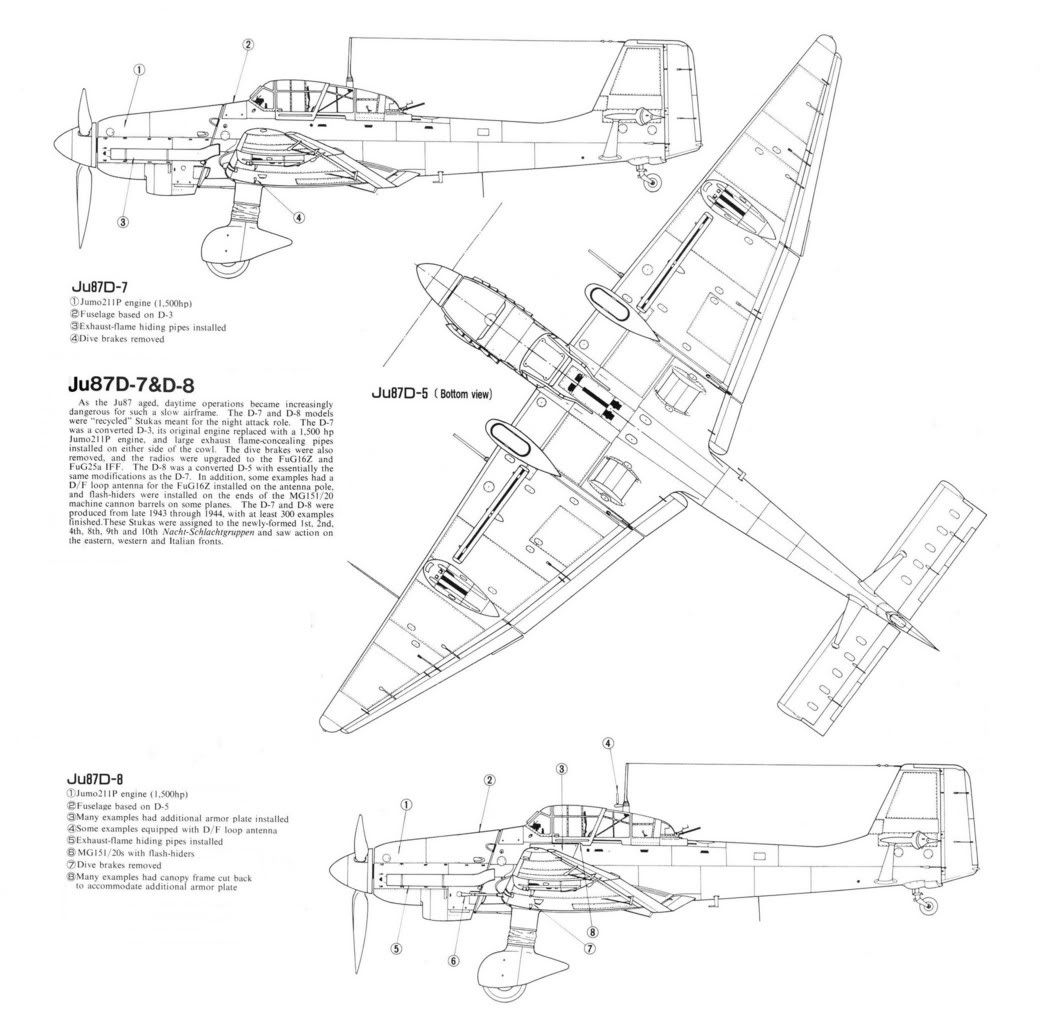
The Ju 87 D-5 was based on the D-3 design and was unique in the Ju 87 series as it had wings 0.6 metres (1 foot) longer than previous variants. The two 7.92 mm MG 17 wing guns were exchanged for more powerful 20 mm MG 151/20s to better suit the aircraft's ground-attack role. The window in the floor of the cockpit was reinforced and four, rather than the previous three, aileron hinges were installed. Higher diving speeds were obtained of 650 kph (408 mph) up to 2,000 m (6,560 ft). The range was recorded as 715 km (443 mi) at ground level and 835 km (517 mi) at 5,000 m (16,400 ft).
The D-6, according to "Operating instructions, works document 2097", was built in limited numbers to train pilots on "rationalised versions". However, due to shortages in raw materials, it did not go into mass production. The D-7 was another ground attack aircraft based on D-1 airframes upgraded to D-5 standard (armor, wing cannons, extended wing panels), while the D-8 was similar to the D-7 but based on D-3 airframes. The D-7 and D-8 were both were fitted with flame dampers, and could conduct night operations.
Production of the D-1 variant started in 1941 with 495 ordered. These aircraft were delivered between May 1941 and March 1942. The RLM wanted 832 machines produced from February 1941. The Weserflug company was tasked with their production. From June to September 1941, 40 Ju 87 Ds were expected to be built, increasing to 90 thereafter. Various production problems were encountered. Just one of the planned 48 was produced in July. Of the 25 the RLM hoped for in August 1941, none were delivered. Only in September 1941 did the first two of the planned 102 Ju 87s roll off the production lines. The shortfalls continued to the end of 1941. During this time, the WFG plant in Lemwerder moved production to Berlin. Over 165 Ju 87s had not been delivered and production was only 23 Ju 87 Ds per month out of the 40 expected. By the spring of 1942 to the end of production in 1944, 3,300 Ju 87s, mostly D-1s, D-2s and D-5s had been manufactured.
Total production amounted to 3639 Ju 87D (592 D-1, 1559 D-3 and 1448 D-5), all built by Weserflug. The last Ju 87 D-5 rolled off the production lines in September 1944.

The Ju 87 E and F proposals were never built, and Junkers went straight onto the next variant. Another variant derived from the Ju 87D airframe, the Ju 87H saw service as a dual-control trainer.
In January 1943, a variety of Ju 87 Ds became "test beds" for the Ju 87 G variants. At the start of 1943, the Luftwaffe test centre at Tarnewitz tested this combination from a static position. Oberst G. Wolfgang Vorwald noted the experiments were not successful, and suggested the cannon be installed on the Messerschmitt Me 410. However, testing continued, and on 31 January 1943, Ju 87 D-1 W.Nr 2552 was tested by Hauptmann Hans-Karl Stepp near the Briansk training area. Stepp noted the increase in drag, which reduced the aircraft's speed to 259 kph (162 mph). Stepp also noted that the aircraft was also less agile than the existing D variants. D-1 and D-3 variants operated in combat with the 37 mm (1.46 in) BK 37 cannon in 1943.
Ju 87G "Gustav"
With the G variant, the aging airframe of the Ju 87 found new life as an anti-tank aircraft. This was the final operational version of the Stuka, and was deployed on the Eastern Front. The reverse in German military fortunes after 1943 and the appearance of huge numbers of well-armoured Soviet tanks caused Junkers to adapt the existing design to combat this new threat. The Hs 129B had proved a potent ground attack weapon, but its large fuel tanks made it vulnerable to enemy fire, prompting the RLM to say "that in the shortest possible time a replacement of the Hs 129 type must take place." With Soviet tanks the priority targets, the development of a further variant as a successor to the Ju 87D began in November 1942. On 3 November, Erhard Milch raised the question of replacing the Ju 87, or redesigning it altogether. It was decided to keep the design as it was, but to upgrade the powerplant to a Jumo 211J, and add two 30 mm (1.18 in) cannon. The variant was also designed to carry a 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) free-fall bomb load. Furthermore, the armoured protection of the Ilyushin Il-2 Sturmovik was copied - a feature pioneered by the 1916-17 origin Junkers J.I of World War I Imperial Germany's Luftstreitkräfte - to protect the crew from ground fire now that the Ju 87 would be required to conduct low level attacks.

Junkers Ju 87G.
[Source: Unknown]
Hans-Ulrich Rudel, a Stuka ace, had suggested using two 37 mm (1.46 in) Flak 18 guns, each one in a self-contained under-wing gun pod, as the Bordkanone BK 3,7, after achieving success against Soviet tanks with the 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon.

These gun pods were fitted to a Ju 87 D-1, W.Nr 2552 as "Gustav the tank killer". The first flight of the machine took place on 31 January 1943, piloted by Hauptmann Hans-Karl Stepp. The continuing problems with about two dozens of the Ju 88P-1, and slow development of the Hs 129 B-3, each of them equipped with a large Bordkanone BK 7,5 cm (2.95 in) cannon in a conformal gun pod beneath the fuselage, meant the Ju 87G was put into production.

Winter Camo
In April 1943, the first production Ju 87 G-1s were delivered to front line units. The two 37 mm (1.46 in) cannons were mounted in under-wing gun pods, each loaded with a six-round magazine of armour-piercing tungsten carbide ammunition. With these weapons, the Kanonenvogel ("cannon-bird"), as it was nick named, proved spectacularly successful in the hands of Stuka aces such as Rudel. The G-1 was converted from older D-series airframes, retaining the smaller wing, but without the dive brakes. The G-2 was similar to the G-1 except for use of the extended wing of the D-5. 208 G-2s were built and at least a further 22 more were converted from D-3 airframes.
Junkers Ju 87 Stuka

37mm Flak 18 mounted on a Junkers Ju 87G.
[Source: Unknown]
Only a handful of production Gs were committed in the Battle of Kursk. On the opening day of the offensive, Hans-Ulrich Rudel flew the only "official" Ju 87 G, although a significant number of Ju 87D variants were fitted with the 37 mm (1.46 in) cannon, and operated as unofficial Ju 87 Gs before the battle. In June 1943, the RLM ordered 20 Ju 87Gs as production variants. The G-1 later influenced the design of the A-10 Thunderbolt II, with Hans Rudel's book, Stuka Pilot being required reading for all members of the A-X project.

Night-harassment variants
The Soviet Air Force practice of harassing German ground forces using antiquated Polikarpov Po-2 and R-5 biplanes at night to drop flares and fragmentation bombs, inspired the Luftwaffe to form its own Störkampfstaffeln (harassment squadrons). On 23 July 1942, Junkers offered the Ju 87 B-2, R-2 and R-4s with Flammenvernichter ("flame eliminators"). On 10 November 1943, the RLM GL/C-E2 Division finally authorised the design in directive No. 1117. This new equipment made the Ju 87 more difficult to detect from the ground in darkness.
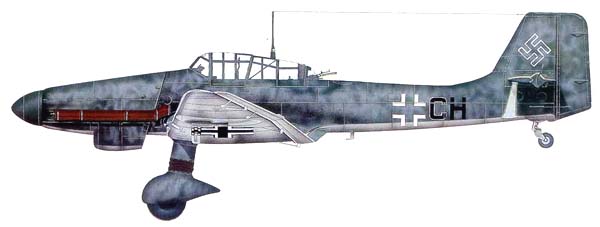
Note the flame suppressors on the exhausts
In the first half of 1943, 12 Nachtschlachtgruppen had been formed, flying a multitude of different types of aircraft, including the Ju 87, which proved itself ideally suited to the low-level slow flying needed.
Unusual operators: